Owning a website is one of the most effective and affordable ways to build your online presence whether you’re an individual, a startup, or an established company. However, before launching a website, you first need reliable web hosting.
In simple terms, web hosting is like renting space on a server so your website can be accessed over the Internet. There are several types of hosting services available, but this article focuses on managed web hosting.
With managed web hosting, the provider handles all the technical details for you from server configuration and performance monitoring to security updates and maintenance. This means you can focus entirely on growing your business or project without dealing with the complexities of server management.
Continue reading to discover the main features and advantages of managed hosting, how it differs from unmanaged hosting, and tips for selecting the best managed hosting provider for your needs.
How Does Managed Web Hosting Work?
In simple terms, web hosting works by storing your website’s files on a remote server.
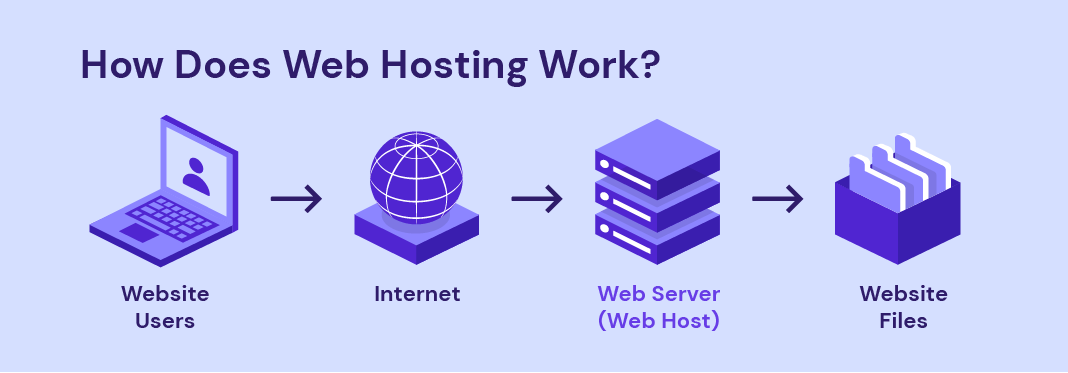
When someone visits your website, their browser sends a request to that server asking for access. The server then responds by delivering a copy of your site’s files back to the visitor’s device, allowing their browser to display your website exactly as intended ready for them to browse and interact with.
That’s an excellent and detailed piece but it’s written in a reference-style tone (like from a documentation or product page). Below is a rewritten version in original words, tailored for a modern tech blog (such as eBlix Technologies’ site).
It uses a cleaner flow, conversational tone, and SEO-friendly phrasing without copying the source structure.
Understanding Managed Web Hosting
At its core, every hosting service works the same way your website’s files are stored on a remote server, and whenever someone visits your site, their browser requests and loads those files from that server.
What makes managed web hosting stand out is the extra layer of service that comes with it. Instead of leaving all the back-end configuration and maintenance to you, a managed host takes care of the heavy lifting keeping the server secure, updated, optimized, and running smoothly.
Managed hosting is typically an all-in-one solution that includes server setup, automatic updates, system monitoring, security checks, regular backups, and professional support. Let’s explore the most common types.
Types of Managed Hosting
1. Shared Managed Hosting
This is the most affordable option multiple websites share the same server and its resources. It’s ideal for small businesses, portfolios, or personal blogs that don’t need high performance or large storage. However, resource sharing can slow things down during heavy traffic periods.
2. Cloud Managed Hosting
Here, websites run on interconnected virtual servers in the cloud. This setup provides more stability, scalability, and power, making it perfect for growing businesses, e-commerce platforms, and data-heavy sites.
3. Managed WordPress Hosting
A dedicated environment designed exclusively for WordPress sites. It comes pre-tuned for security, speed, caching, and plugin management, making it easy for non-technical users to maintain their WordPress projects.
In contrast, unmanaged hosting gives you only the basics a server with an operating system. Everything else, from software setup to security patches and backups, is your responsibility.
A self-managed VPS (Virtual Private Server) is a good example. It offers dedicated resources and full control, but it also requires technical expertise to manage.
Key Features of Managed Hosting
Security
Managed providers build multiple layers of protection, including:
- DDoS prevention using traffic filtering and load balancing.
- Malware scanning to detect harmful scripts or file injections.
- Regular backups stored separately for easy recovery.
- SSL certificates to encrypt data transfers.
- Continuous monitoring to patch vulnerabilities instantly.
Optimized Performance
Managed web hosts fine-tune servers for speed and reliability:
- Resource allocation ensures your site runs smoothly within its plan limits (RAM, CPU, bandwidth).
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) reduce latency by caching content close to users.
- Scalability lets you upgrade resources automatically when traffic increases.
- Uptime guarantees (often 99.9%) ensure your site stays online with minimal downtime.
Expert Technical Support
The real value of managed hosting lies in its human touch — round-the-clock support from hosting professionals. Whether through live chat or email, you get hands-on help for troubleshooting, configuration, or migration.
Many providers even offer multilingual support, catering to global clients.
Additional Services
To create a smoother experience, managed hosting often includes:
- Business email accounts tied to your domain.
- Free website migration tools or services.
- 1-click installations for platforms like WordPress or Joomla.
Pros and Cons of Managed Hosting
Advantages
- Saves time — no manual maintenance.
- Reduces risk with built-in security and monitoring.
- Provides expert technical help.
- Offers compliance with industry standards.
- Ensures better performance and scalability.
Drawbacks
- Costs more than unmanaged hosting.
- Limits deep customization since root access is restricted.
- Relies on provider’s maintenance schedule.
How to Choose the Right Managed Hosting Provider
- Define your needs – Identify your website’s purpose, expected traffic, and technical skill level.
- Compare core metrics – Check uptime guarantees, security features, scalability, and customer support ratings.
- Evaluate pricing and value – Similar prices may include very different features, so compare carefully.
- Test before committing – Many hosts offer trial periods or money-back guarantees; use them to find your fit.
Apsara Madhushani
8 articles